Burial Chambers is a level from Tomb Raider 4.
Pictures[]
04.01 - Scarab with wings
Lara is looking at a lever and two ramheaded sfinxes. Behind that there is a scarab, wings and some rays.
The rays came from the famous royal chair of Tutankhamun. These are the rays of the Aten. Tutankhamun was the son of Pharaoh Akhenaten and an yet unknown wife (possible Kiya, Nefertiti or one of the children of Akhnaten). Pharaoh Akhenaten was once called Amenhotep but changed his name because he worshipped the god Aten in favour, rather then Amun who is the patron god of Thebes. Tutankhaten changed his name to Tutankhamun.
After Akhenaten died, his wife Nefertiti reigned Egypt as king. Then Meritaten reigned together with Nefertiti as great Royal Wife and as a Pharaoh or possible with Smenkhare (or Smenkhare was Nefertiti) and then Tutankhamun reigned. In this time frame it is obvious that the tomb treasure of Tutankhamun has some of the “Amarna” treasure with the god Aten on it.
But the famous chair of Tutankamun has the rays of Aten on it and his older form of his name: Tutankhaten.
04.02 - Golden cartouches and golden scarab
1) The golden scarab with wings represents the reign name of Tutankhamun, called Neb-Kheperu-Re. It is from a perfume box of Tutankhamun called by Howard Carter 240bis. It is not the frond but the side. The perfume box shows the four stages of a young king to be mature and old king. It’s a shame that would not happen. (picture from here: https://www.worthpoint.com/worthopedia/boehm-porcelain-tutankhamun-perfume-153601455)
2) The cartouches reads the same but the sun disc is not visible. These come from the first shrine (1st of five) of Tutankhamun on the left side of the shrine. The hieroglyphics say: Nebet-tawi Neb-Kheperu-Re. Nebet-Tawi translates as “King of the two lands”. You can read more here of the translation of the kingsname.
04.03 - the boy king
It is parfume box again. It shows here the boy king seated on a sign and under the blessed sun with two ureaus snakes with ankhs. It is a secret writing of the name Neb-Kheperu-Re. You can see it is a boy king because of the shaven head and one thick braid.
04.04 - The rays of Aten
Lara looks at the Aten disc. It shows a ureaus snake on front, it looks like an archaic 3d picture, rays that ends in hands holding ankhs (life sign) for the king. It came from the famous chair of Tutankhamun.
04.05 - Pot
Lara is looking at a pot. But the texture came from a pectoral of General Wendjebauendjed buried in the Tanis tomb of the 21/22 dynasty some 100 years after Tutankhamun I think. It was discovered by Pierre Montet during the second world war. Found on flickr: https://www.flickr.com/photos/amthomson/42492967465/in/faves-24729615@N00/
04.06 - Vulture
On the wall is a vulture. It represents the goddess Nekhbet. It is an amulet of pharaoh Tutankhamun. In her paws the goddess has some symbols: “shen-rings”, it’s meaning is eternal protection. The cartouche is also a “shen” but with hieroglyphics in it.
04.07 - Coffin
It is a coffin of an ancient Egyptian mummy. It can be found at the British museum (right one). It is Henutmehyt, a Theban priestess from the 19th dynasty (the Ramsesid era)
04.08 - Hawk-god with sun disc
It is the god Ra-Horakhty or a combination of Horus-of-the-horizons (Akhet means horizon, the ‘y’ is plural) and Ra, the sun god.
In later Egyptian mythology, Ra-Horakhty was more of a title or manifestation than a composite deity. It translates as “Ra (who is) Horus of the Horizons”. It was intended to link Horakhty (as a sunrise-oriented aspect of Horus) to Ra. It has been suggested that Ra-Horakhty simply refers to the sun’s journey from horizon to horizon as Ra, or that it means to show Ra as a symbolic deity of hope and rebirth
I think it is from the Abu Simbel temple in Upper-Egypt near the border of Sudan.
04.09 - Yet another Scarab with wings.
Lara is looking at a scarab with wings. It is the throne name of king Tutankhamun or Neb-Kheperu-Ra. It is one of the many treasures of King Tut.
04.10 - Inside the coffin
Unknown coffin.
04.11 - Woman with baskets.
This comes from the Mastaba of Ti in Saqqara, Egypt. Ti was a friend of the pharaoh and build a gigantic mastaba during the 5th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt. The woman holding baskets with fruit and other things.
04.12 - Man offering to diseased
The man is offering some mirre to two diseased. But I couldn’t find it.
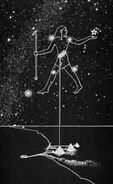
04.13 - The hand of Orion amulet
The Hand of Orion connects this level to the past level: Tomb of Seth. In that level you encounter some star deities of the Temple of Dendera.
The Orion constellation was connected with the god Sah which was a form of Osiris. In the 90s there was a book of the Orion Mystery. In it the three pyramids of Gizeh would be connected with the Orion constellation (or Sah). Maybe this could be some inspiration. I would recommend the book to read.
04.14 - The hand of Sirius amulet
Sirius is a bright star in the sky. Sopdet became Sothis in the Greek language and later Sirius.. It played a huge role in ancient Egypt. It was seen as the goddess Sopdet which would be a form of Isis. Isis and Osiris are a couple and Horus was their child. The sun of Sopdet and Sah is Sopdu.
The rise of Sirius and the sun during the summer (juli/august) marks a new year of the ancient Egyptians. But there were two calendar systems: the ciivil one based on the moon and later on the sun (360 days + 5 special days) and the one based on the Sirius used by the priests.
(The right one from Temple of Hathor in Dendera, left one is Anuket)
04.15 - The golden serpent amulet
It looks a bit like the diadem of Tutankhamun.